Exploring the connection between financial assistance for medical care and medical collections
August 24, 2022 / Source: CFPB
In 2020, Americans spent $4.1 trillion on health care . Despite private insurance coverage and government programs like Medicare and Medicaid that cover all or part of the cost of medical treatments, consumers continue to incur significant medical expenses. By 2028, healthcare-related expenses are projected to reach $6.2 trillion.
The Affordable Care Act (ACA) requires nonprofit hospitals to establish financial assistance policies—often known as “charity care”1—for consumers who are unable to pay for these expenses. In this blog, we explore the connection between eligibility for these financial assistance programs and the prevalence of medical collections using data from the CFPB’s Making Ends Meet survey.
The prevalence of medical collections
Many Americans, especially those with lower incomes, can’t afford to pay the high cost of medical care, and unpaid medical debts may eventually end up in collections and on consumers’ credit reports. The ACA prohibits nonprofit hospitals from reporting medical debts as collections to credit reporting companies, or from selling the debt to another party, without first trying to determine whether the patient would be eligible for their financial assistance policies. We find, however, that even with these policies in place a large percentage of low-income consumers in 2018 had at least one medical collection on their credit reports.
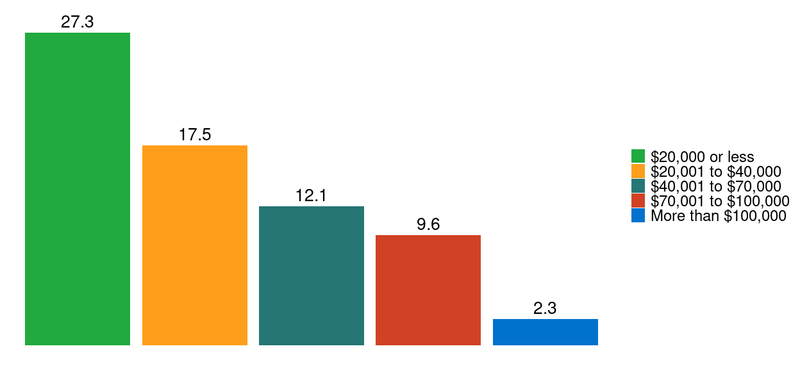
The data indicate that as household incomes decrease, a higher percentage of consumers have medical collections. Figure 1 shows that 17.5 percent of those with household earnings between $20,001 and $40,000 in 2018 had at least one medical collection on their credit report. This fraction grows to 27.3 percent for people whose household income was less than $20,000.
Figure 1: Percentage of households with at least one medical collection in December 2018, by income
Financial assistance eligibility and medical collections
Some state laws have established eligibility thresholds as a percentage of federal poverty levels, which are based on both income and household size. Consequently, both factors are often relevant when determining a person’s eligibility for financial assistance. While we don’t have complete data on household size from the Making Ends Meet survey, we do know whether children are present in a household. Combining this information with data on income provides further insight into the relationship between financial assistance eligibility and the prevalence of medical collections on consumers’ credit reports.
Figure 2 shows that among people in households with children and with incomes under $40,000—many of whom would fall under 200 percent of the federal poverty threshold for their household size2—38.1 percent had at least one medical collection on their credit report in December 2018. This is nearly three times the rate for people without children earning the same amount.
Figure 2: Percentage of households with at least one medical collection in December 2018 by income and household composition
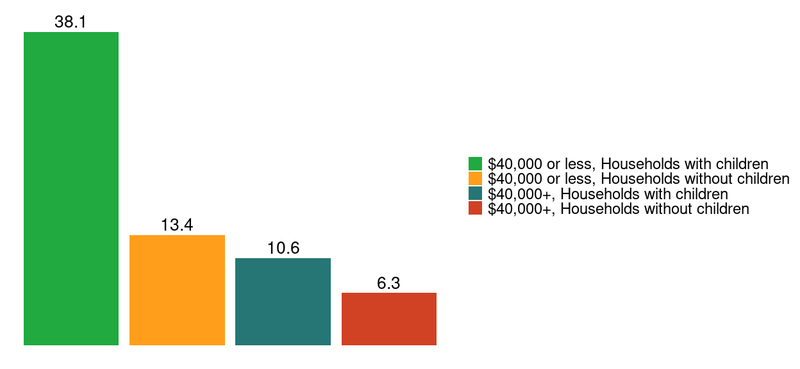
Regional differences in medical collection outcomes
Different outcomes also arise based on the region of the country consumers live in. Figure 3 shows that the Northeast (depicted with red) has the fewest medical collections per person and the lowest average collection balances among those with one collection or more. The South (in green) has the highest percentage of individuals with a medical collection, while the number of collections and total amount owed are highest in the Midwest (in yellow).
Some of the regional differences may be explained by differences in the adoption of Medicaid expansion, differences in income levels, or differences in the rates of medical insurance coverage. State laws and programs related to the provision of financial assistance also appear to differ significantly across the country. Further research is needed to determine the extent to which the different outcomes in Figure 3 are also the result of differences in state financial assistance policies.
Figure 3: Medical collection prevalence and size by region
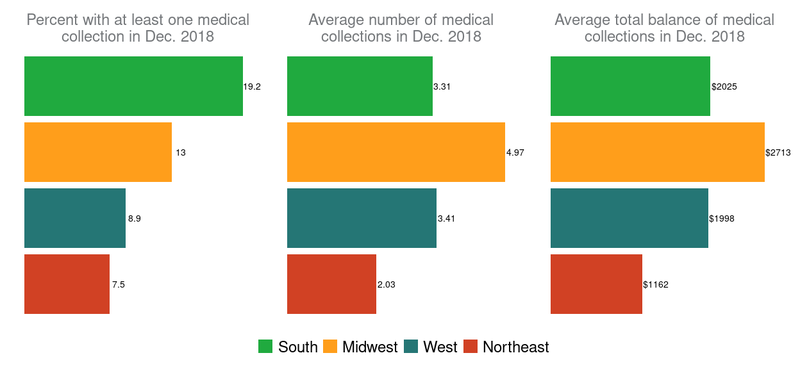
The average number of medical collections and the average balance of medical collections are calculated for those with at least one medical collection on their credit records in December 2018
Impact of removing some medical collections from credit records
The three nationwide credit reporting companies – Experian, Equifax, and TransUnion – have announced changes in how unpaid medical bills will appear on consumer credit reports. In July 2022, all three began removing paid medical collections from credit reports, and starting in 2023 they will no longer report medical collections below $500. The companies have also increased the amount of time after which a medical bill can appear on a credit report from six months to one year.
These changes have the potential to improve the credit of low-income individuals who – despite possible eligibility for financial assistance – have medical collections on their credit reports. However, many low-income consumers are still unlikely to benefit because their existing medical bills exceed the $500 threshold. Among consumers with medical collections on their credit records, 48 percent of those making less than $40,000 per year in 2018 had at least one collection for over $500 at the time. Collections like these will continue to weigh on consumers’ credit outcomes. Credit reporting changes notwithstanding, access to financial assistance will continue to be important for the lowest income households.
Conclusion
Even though many low-income consumers are eligible to receive financial assistance, a large percentage of consumers with low incomes have medical collections on their credit reports. We lack the data to identify debts incurred from nonprofit hospitals, so many of these debts may come from for-profit and other providers. Nonprofit hospitals, however, make up approximately 49 percent of all hospitals . These hospitals must provide financial assistance and other community benefits in exchange for the significant tax benefits they receive, yet our results suggest that many consumers do not receive the financial assistance they need.
Different regions of the country also experience very different outcomes with medical collections, some of which may be attributed to differences in state laws and other programs regarding financial assistance. Future research could explore the extent to which differences in legislative and regulatory environments influence the provision of financial assistance and lead to better financial outcomes for consumers.
The views expressed here are those of the authors and do not necessarily reflect the views of the Consumer Financial Protection Bureau. Links or citations in this post do not constitute an endorsement by the Bureau.
Footnotes
- We use the term required financial assistance or financial assistance instead of the term charity care because they more accurately reflect that hospitals benefitting from various federal and state tax exemptions have a legal requirement to provide financial assistance to those who cannot afford the cost of care.
- Some states use 200% of the federal poverty level to establish eligibility for financial assistance. The $40,000 cutoff we use here is roughly twice the 2018 poverty level for a household of three.